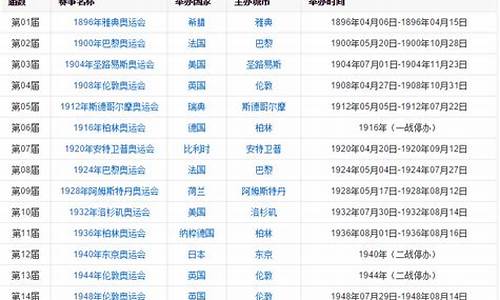
1.奥运五环的含义(哪种颜色代表哪一洲)英语
2.奥运五环的意义?
3.求一篇英语关于奥运五环的文章

奥运会会旗和奥运会圣火的含义
The OLYMPIC FL
现代奥运会创始人顾拜旦于1913-1914年间设计了奥运会的会旗。它由5个奥林匹克环从左至右套接而成,可以是单色,也可以是蓝、黄、黑、绿、红5种颜色。最初的解释是五种颜色代表各国国旗的颜色,后来又将5个不同颜色的圆环解释为五大洲的象征。1920年,奥林匹克旗第一次飘扬在安特卫普夏季奥运会体育场。这届奥运会后,历届奥运会开幕式上由上届举办城市转交此旗,由举办城市保存,比赛期间主运动场仅悬挂代用品。
Baron de Coubertin designed the Olympic Flag in 1913-14. It has five interlocking rings (blue, yellow, black, green and red) on a white background. The ring's colours were based on the knowledge that at least one of these colours is on every flag of each participating country. The five interlocking rings represent the union of the five continents and the meeting of the athletes of the world at the Olympic Game.
The Olympic Flag was used for the first time in the 7th Olympiad in Antwerp, Belgium in 1920. It is paraded during the opening ceremony of each Game. At the end of the Games, the Olympic Flag is presented to the next host city by the Games host city.
奥运五环的含义(哪种颜色代表哪一洲)英语
1951年之前,官方手册曾指奥运五环分别象征着五个大洲,即:蓝色代表欧洲;黑色代表非洲;红色代表美洲;**代表亚洲;绿色代表大洋洲;但之后这句话从官方手册上移除,因为没有证据显示皮埃尔创作五环有过这样的意思。
奥林匹克标志象征五大洲和全世界的运动员在奥运会上相聚一堂,充分体现了奥林匹克主义的内容," 所有国家—一所有民族"的“奥林匹大家庭"主题。它不仅代表着五大洲全世界运动员在奥林匹克旗帜下的团结和友谊,而且强调所有运动员应以公正、坦诚的运动精神在比赛场上相见。
扩展资料:
奥林匹克五环
奥林匹克五环,五个互扣的环圈,五环的颜色自左至右为蓝、黄、黑、绿、红,也可用单色绘制,而底色为白色。奥林匹克五环于1913年由前国际奥林匹克委员会、现代奥林匹克运动会创始人皮埃尔·德·顾拜旦设计,因以五色能概括各会员国国旗的颜色而选定,但之后对五环赋予更多内涵
19年,国际奥委会出版的《奥林匹克评论》中指出:五环象征五大洲的团结,全世界的运动员以公正、坦率的比赛和友好的精神在奥运会上相见。
参考资料来源:百度百科-奥林匹克标志
奥运五环的意义?
随着奥林匹克运动的发展,奥运五环已成为奥林匹克精神与文化的形象代表,国际奥委会选择五个相连的圆环作为其标志,并选择了相应的色彩。五个圆环代表五大洲:大洋洲、非洲、美洲、亚洲和欧洲。更深一层的意思是代表着全世界的运动员都聚集在奥林匹克运动会上。
朴素的白色背景寓意着和平。
它是1914年国际奥委会成立20周年庆祝大会时,由创始人古柏丁爵士所提。在听了顾拜旦对五环标志的说明后,会议确定将奥林匹克五环和奥林匹克旗作为奥林匹克标志。并制成会旗,于1920年第七届奥运会正式出现,开始使用至今。
五种颜色从左到右分别是:上方三个蓝、黑、红,下方黄和绿。这五种颜色都为各国国旗上的常见颜色,最初没有被赋予特殊含义。后来将5个不同颜色的圆环解释为五大洲的象征。
蓝 =欧洲(Europe) 黄 =亚洲( Asia) 黑 =非洲(Africa) 绿 =大洋州(Oceania)
红 =美洲( America)
奥运五环是国际奥委会的官方专用标志
求一篇英语关于奥运五环的文章
奥运五环代表着五大洲(天蓝色代表欧洲,**代表亚洲,黑色代表非洲,草绿色代表澳洲,红色代表美洲)五个不同颜色的圆环连接在一起象征五大洲的团结互助、相亲相爱,象征世界五大洲不同肤色的人民能够友好相处,象征五大洲和全世界的运动员在奥运会上相聚一堂,充分体现了奥林匹克主义的内容,所有国家—所有民族的”奥林匹克大家庭“主题。
奥林匹克标志 (Olympic Logo /Symbole Olympique/Olympic Rings)是由皮埃尔·德·顾拜旦先生于1913年构思设计的,是由《奥林匹克宪章》确定的,也被称为奥运五环标志,它是世界范围内最为人们广泛认知的奥林匹克运动会标志。它由5个奥林匹克环套接组成,有蓝、黄、黑、绿、红5种颜色。环从左到右互相套接,上面是蓝、黑、红环,下面是是黄、绿环。整个造形为一个底部小的规则梯形。
奥林匹克五环标志,它由5个奥林匹克环套接组成,由蓝、黑、红、黄、绿5种颜色。环从左到右互相套接,上面是蓝、黑、红环,下面是是黄、绿环。整个造形为一个底部小的规则梯形。根据奥林匹克宪章,五环的含义不仅代表着五大洲全世界运动员在奥林匹克旗帜下的团结和友谊,同时强调着所有运动员应以公正、坦诚的运动精神在比赛场上相见。
奥运五环
1.The Olympic Games olympic flag is the management formulates in GuBaidan under. Five links be blue, black, are respectively red, yellow,the green, three links in on, two links in under, are linked together,tight association in same place. Does obeisance the day regarding thiplanation according to the attendance, five links "in the symbolicworld acknowledged the Olympics movement, and prepares to attend theOlympic Games the five continents, but the sixth kind of color white -flag bottom color, Italy refers to all countries all without a singleexception to be able to attend the competition in under the oneselfcountry flag". Afterwards some people explained that, IOC used atfirst blue, black, is red, yellow, the green took five links thecolors were because it could represent participates in the IOC allcountries national flag at that time the color. The 7th session ofOlympic Games got up from 1920, five links five kind of colorssymbolized the five continents: The blue color represents Europe,black Italy refers to Africa, red symbolizes the Americas, the yellowsymbolizes Asia, but the green explains makes Australia. In 13 theIOC published conference proceeding "the Olympics Forum" emphasizedthat, "The conference symbol and the meeting pennant five linksmeaning is symbolizing five continents' unity, world athlete by fair,frank competition and friendly spirit, meets at the Olympic Games."
奥运会五环旗是在顾拜旦主持下制定的。五环分别为蓝、黑、红、黄、绿色,三环在上,两环在下,环环相扣,紧紧联在一起。按照顾拜旦对此的解释,五环“象征世界上承认奥林匹克运动、并准备参加奥林匹克竞赛的五大洲,而第六种颜色白色——旗帜的底色,意指所有国家都毫无例外地能在自己国家的旗帜下参加比赛”。 后来有的人解释说,国际奥委会最初用蓝、黑、红、黄、绿色作为五环的颜色是因为它能代表当时参加国际奥委有国家国旗的颜色。自1920年第7届奥运会起,五环的五种颜色象征五大洲:蓝色代表欧洲,黑色意指非洲,红色象征美洲,**标志着亚洲,而绿色喻作澳洲。 13年国际奥委会会刊《奥林匹克论坛》则强调:“会徽和会旗的五环含义是象征着五大洲的团结,全世界的运动员以公正、坦率的比赛和友好的精神,在奥运会上相见。”
2.The flag features the emblem of the Olympic Games — five interlocking rings (blue, yellow, black, green, and red respectively) on a white field. This was originally designed in 1913 by Baron Pierre de Coubertin, the founder of the modern Olympic Games, but gained widespread popularity due to its promotion by Nazi Germany [1]. Upon its initial introduction, de Coubertin stated the following in the August, 1913 edition of Revue Olympique:
The emblem chosen to illustrate and represent the world Congress of 1914 ...: five intertwined rings in different colours - blue, yellow, black, green, red - are placed on the white field of the paper. These five rings represent the five parts of the world which now are won over to Olympism and willing to accept healthy competition.
In his article published in the "Olympic Revue" the official magazine of the International Olympic Committee in November 1992, the American historian Robert Barney explains that the idea of the interlaced rings came to Pierre of Coubertin when he was in charge of the USA ( Unión des Societes Fran?aise de Sports Athletiques): The emblem of the union was two interlaced rings (like the typical interlaced marriage rings) and originally the idea of Swiss psychiatrist Carl Jung because for him the ring meant continuity and the human being. [2]
“ The Olympic flag [...] has a white background, with five interlaced rings in the centre : blue, yellow, black, green and red [...] This design is symbolic ; it represents the five continents of the world, united by Olympism, while the six colours are those that ear on all the national flags of the world at the present time. ” (1931) Textes choisis II, p.470.
The 1914 Congress had to be suspended due to the outbreak of World War I, but the flag and emblem were later adopted. They would first officially debut at the VIIth Olympiad in Antwerp, Belgium in 1920.
The emblem's popularity and widespread use began during the lead-up to the 1936 Summer Olympics in Berlin. Carl Diem, president of the Organizing Committee of the 1936 Summer Olympics, wanted to hold a torchbearers' ceremony in the stadium at Delphi, site of the famous oracle, where the Pythian Games were also held. For this reason he ordered construction of a milestone with the Olympic rings carved in the sides, and that a torchbearer should carry the flame along with an escort of three others from there to Berlin. The ceremony was celebrated but the stone was never removed. Later, two British authors Lynn and Gray Poole when visiting Delphi in the late 1950?s saw the stone and reported in their "History of the Ancient Games" that the Olympic rings design came from ancient Greece. This has become known as "Carl Diem's Stone". [3] [4]. This created a myth that the symbol had an ancient Greek origin. The rings would subsequently be featured prominently in Nazi images and theatrics in 1936 as part of an effort to glorify the Third Reich and claim a noble and ancient lineage.
The current view of the International Olympic Committee is that the flag "reinforces the idea" that the Olympic Movement is international and welcomes all countries of the world to join. [5] Some literature, such as "The World Encyclopedia of Flags" by Alfred Znamierowski, state that each ring represent the five continents. Using this scheme, the Americas are viewed as a single continent, and Antarctica is omitted.
As can be read in the Olympic Charter, the Olympic symbol represents the union of the five continents and the meeting of athletes from throughout the world at the Olympic Games. However, no continent is represented by any specific ring. Though colourful explanations about the symbolism of the coloured rings exist, the only connection between the rings and the continents is that the number five refers to the number of continents.